Blog
How to
Build an AI Chatbot from Scratch
Building an AI chatbot from scratch involves multiple stages:
planning, designing conversation flow, selecting technology, coding, training
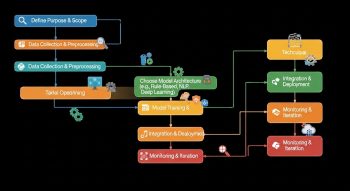
Building an AI chatbot from scratch involves multiple stages: planning, designing conversation flow, selecting technology, coding, training the AI, and deploying it for real-world use. Doing it yourself gives flexibility to customise the chatbot’s behaviour, integrate specific knowledge, and add features like multi-turn conversations or contextual awareness.
1. Define Your Chatbot’s Purpose
Before coding, define what your chatbot should do. This will shape your design and technology choices:
-
Customer support chatbot: Answer FAQs, track orders, and provide troubleshooting.
-
Personal assistant: Schedule appointments, reminders, or provide information.
-
Entertainment chatbot: Chat for fun, tell jokes, and role-play characters.
-
Education chatbot: Help with learning, answer questions, and provide tutorials.
Tip: The clearer your goal, the easier it will be to design workflows and train your chatbot.
2. Design Conversation Flow
Map out how the chatbot will interact with users:
-
Identify user intents (e.g., greeting, product inquiry, complaints).
-
Define responses for each intent.
-
Plan multi-turn conversations for complex queries.
-
Include fallback responses for unknown inputs.
Example conversation flow:
| User Input | Chatbot Response |
|---|---|
| “Hi” | “Hello! How can I help you today?” |
| “Order status” | “Please provide your order number.” |
| Unknown | “Sorry, I didn’t understand that. Can you rephrase?” |
Tools like draw.io or Miro can help visualise the flow.
3. Choose Your Technology Stack
There are two main approaches: rule-based and AI-powered.
A. Rule-Based Chatbots
-
Respond based on predefined rules and keywords.
-
Simpler but less flexible.
-
Technologies:
-
Python + Regex / if-else statements
-
Node.js + NLP libraries
-
Platforms: Dialogflow, Rasa (can also support AI features)
-
B. AI-Powered Chatbots
-
Use machine learning / natural language models to understand user input.
-
Can handle dynamic queries and complex conversations.
-
Technologies:
-
OpenAI GPT API (GPT-3/4 models)
-
Hugging Face Transformers (BERT, GPT-Neo, GPT-J)
-
Python frameworks: TensorFlow, PyTorch
-
Rasa Open Source for AI chatbots
-
4. Setting Up Your Development Environment
-
Install Python 3.x.
-
Install essential libraries:
-
For web integration: install Flask or Django for the backend, or Node.js for JavaScript.
-
Optionally, set up a database (SQLite, PostgreSQL, MongoDB) for storing conversation logs or context.
5. Build a Basic Rule-Based Chatbot
Example in Python:
Cons: Limited understanding, cannot handle complex conversations.
6. Build an AI-Powered Chatbot Using OpenAI GPT
Step 1: Get API Key
-
Sign up at OpenAI and generate an API key.
Step 2: Write a Python Script
Step 3: Test Your Chatbot
-
Run the script, type messages, and get AI responses.
-
Type “exit” to quit the chat.
7. Add Custom Knowledge
If you want the chatbot to have domain-specific knowledge:
-
Preload data: FAQs, product details, manuals.
-
Embed knowledge base: Use vector databases like Pinecone or Weaviate.
-
Fine-tune the AI model: Train the model with your data (OpenAI fine-tuning or Hugging Face models).
Example:
8. Integrate the Chatbot into Applications
-
Web: Use Flask/Django backend and JavaScript chat widget.
-
Mobile apps: Use HTTP requests in Swift (iOS) or Kotlin (Android).
-
Messaging platforms: Integrate with WhatsApp, Telegram, or Messenger using their APIs.
Example: JavaScript fetch to call GPT API:
9. Add Personality and Rules
-
Define tone and style: friendly, formal, humorous.
-
Add fallback responses for unknown queries.
-
Include safety filters to prevent harmful outputs.
10. Testing and Optimization
-
Test across multiple devices and scenarios.
-
Collect conversation logs to improve responses.
-
Update the knowledge base regularly.
-
Monitor user engagement and response quality.
11. Advanced Features
-
Multi-turn context: Maintain conversation context for longer interactions.
-
Voice integration: speech-to-text and text-to-speech.
-
Personalisation: Tailor responses based on user history or preferences.
-
Analytics: Track queries, satisfaction, and common issues.
-
Integration with other APIs: weather, maps, e-commerce, or databases.
12. Deployment Options
-
Cloud hosting: AWS, Google Cloud, Azure.
-
Serverless platforms: Vercel, Netlify, or Heroku.
-
Self-hosted: Raspberry Pi or local servers for small projects.
-
Embed a chatbot into websites, mobile apps, or messaging platforms.
13. Benefits of Building Your Own Chatbot
-
Full customisation of features and personality.
-
Can handle domain-specific tasks.
-
Cost-effective compared to third-party solutions in the long run.
-
Scalable across multiple platforms.
-
Great learning experience for AI, NLP, and programming.
Conclusion
Building an AI chatbot from scratch requires planning, designing conversation flow, selecting technology, coding, training, and deployment. You can start simple with rule-based logic and scale to an AI-powered chatbot using models like GPT. Adding custom knowledge, personality, and multi-turn context makes your chatbot more intelligent and engaging.
He is a SaaS-focused writer and the author of Xsone Consultants, sharing insights on digital transformation, cloud solutions, and the evolving SaaS landscape.