Blog
How Long
Does It Take to Develop an AI Chatbot? A Complete Project Timeline
Introduction Contents hide 1 Introduction 2 The Short Answer:
Estimating Timeframes by Complexity 2.1 1. Basic Rule-Based
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital transformation, one question dominates boardroom discussions and product roadmaps alike: how long does it take to develop an AI chatbot? As businesses race to integrate Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) into their customer service and operational workflows, understanding the temporal investment is just as critical as budgeting the financial cost.
The answer, unfortunately, is rarely a simple number. While a basic customer support bot based on rigid decision trees might be deployed in weeks, a fully custom, context-aware AI agent capable of executing complex transactions and learning from user interactions can take several months. The gap between a “demo” and an enterprise-ready solution is vast, filled with critical phases of data sanitization, security compliance, and rigorous reinforcement learning.
This guide serves as a definitive project timeline for CTOs, Product Managers, and business leaders. We will dismantle the development lifecycle phase by phase, distinguishing between rapid MVP launches and full-scale enterprise deployments, ensuring you have a realistic roadmap for your AI initiative.
The Short Answer: Estimating Timeframes by Complexity
To set immediate expectations, we must categorize the project based on intelligence and integration depth. Development time correlates directly with the sophistication of the Natural Language Processing (NLP) capabilities and the backend infrastructure.
1. Basic Rule-Based Chatbot (2 to 4 Weeks)
These are not “true” AI in the generative sense. They rely on pre-defined scripts and button-based navigation. Development is primarily focused on mapping conversation flows (decision trees) rather than training models.
- Use Case: FAQ handling, basic lead capture.
- Primary Time Sink: Content creation and script logic.
2. Intermediate AI Assistant / RAG Implementation (1 to 3 Months)
This category represents the modern standard for most businesses. By utilizing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), these bots connect an LLM (like GPT-4 or Claude) to your specific company knowledge base. They understand context but operate within strict guardrails.
- Use Case: Customer support, internal HR assistants, document analysis.
- Primary Time Sink: Data vectorization, prompt engineering, and API integration.
3. Advanced Custom AI Agent (3 to 6+ Months)
This is a bespoke solution involving fine-tuning open-source models (like Llama 3 or Mistral) on proprietary datasets, hosting models on private infrastructure, and deep integration into legacy ERP/CRM systems with autonomous execution capabilities.
- Use Case: Regulated industries (FinTech, Healthcare), complex workflow automation.
- Primary Time Sink: Model fine-tuning, security auditing, and extensive User Acceptance Testing (UAT).
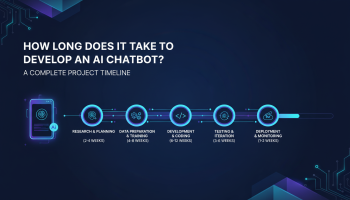
Phase-by-Phase Timeline Breakdown
A professional software development lifecycle (SDLC) for an AI chatbot involves six distinct phases. Rushing through these—particularly the discovery and testing phases—is the leading cause of project failure.
Phase 1: Discovery and Strategic Scope (1–2 Weeks)
Before a single line of code is written, the foundation must be laid. This phase defines the “brain” of the chatbot.
- Stakeholder Alignment: Determining the primary KPIs (e.g., call deflection rate vs. customer satisfaction score).
- Persona Design: Defining the bot’s tone of voice, personality, and ethical boundaries.
- Use Case Mapping: Identifying the top 20% of queries that make up 80% of volume.
- Technical Feasibility Audit: assessing current data cleanliness and API availability.
Phase 2: Conversational Design and Prototyping (2–3 Weeks)
Unlike traditional UI/UX, AI interfaces are conversational. This phase involves designing the “Happy Path” and the inevitable edge cases.
- Flowcharting: Visualizing complex dialogue trees for fallback scenarios.
- Prompt Strategy: Drafting the system prompts that will govern the AI’s behavior.
- Mockups: Designing the chat widget interface within the brand guidelines.
Phase 3: Development and Integration (4–8 Weeks)
This is the most variable phase, depending heavily on whether you are using a low-code platform or building a custom backend with Python/LangChain.
Frontend Development
Developers build the chat interface (Web, Mobile App, WhatsApp, Slack) ensuring low latency and responsiveness.
Backend Engineering
This involves setting up the orchestration layer. It includes:
- Vector Database Setup: Indexing your knowledge base (PDFs, SQL databases, documentation) for the AI to retrieve.
- API Connectors: Building bridges to tools like Salesforce, HubSpot, or Shopify so the bot can fetch order statuses or update user details.
- Context Management: Programming the memory window so the bot remembers what the user said three messages ago.
Phase 4: AI Training and Fine-Tuning (3–6 Weeks)
This phase differentiates a generic wrapper from a high-value asset. It is not just about “feeding data”; it is about curation.
- Data Sanitation: Removing PII (Personally Identifiable Information) and conflicting data from the training set.
- Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT): If building a custom model, this involves training the model on specific Q&A pairs to adopt industry-specific jargon.
- RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback): Human testers rate the bot’s responses to improve accuracy and reduce hallucinations.
Phase 5: Quality Assurance and Compliance Testing (2–4 Weeks)
AI introduces non-deterministic risks. Testing must be exhaustive.
- Adversarial Testing (Red Teaming): Trying to “break” the bot by forcing it to say offensive or incorrect things (Jailbreaking attempts).
- Hallucination Checks: Verifying that the bot says “I don’t know” rather than inventing facts.
- Load Testing: Ensuring the infrastructure can handle concurrent users without high latency.
- Compliance Review: GDPR/CCPA checks, ensuring data encryption and consent management.
Phase 6: Deployment and Post-Launch Optimization (Ongoing)
Deployment is not the finish line; it is the starting line for real-world learning.
- Soft Launch (Beta): Rolling out to internal staff or 5% of traffic.
- Hypercare Period (2 Weeks): Developers monitor logs in real-time to fix immediate bugs.
- Continuous Improvement: Reviewing conversation logs weekly to update the knowledge base and refine system prompts based on actual user queries.
Key Factors That Inflate Development Time
When asking how long does it take to develop an AI chatbot, you must account for these common bottlenecks that can delay timelines by weeks or months.
1. Data Readiness
AI is only as good as the data it accesses. If your company’s documentation is scattered, outdated, or contradictory, significant time will be spent auditing and cleaning content before development can begin.
2. Complex Integrations
Reading data is easy; writing data is hard. If the bot needs to perform actions—like processing a refund or scheduling an appointment—the security protocols and API testing required are significantly higher. Two-way sync with legacy systems often introduces unforeseen technical debt.
3. Legal and Security Reviews
For enterprise organizations, getting approval for where the data is processed (e.g., Azure OpenAI vs. on-premise Llama) can stall projects. Security questionnaires and penetration testing are mandatory steps that cannot be rushed.
Build vs. Buy: The Impact on Time-to-Market
Your choice of development strategy is the single biggest lever for speed.
- SaaS Platforms (The “Buy” Approach): Using platforms like Intercom Fin or Zendesk AI allows for deployment in 2–4 weeks. However, you are limited by their features and customization options.
- Custom Development (The “Build” Approach): working with a development agency to build on LangChain, Pinecone, and OpenAI APIs takes 3–6 months. The upside is total ownership of IP, unlimited flexibility, and no vendor lock-in regarding the underlying model.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I build an AI chatbot in less than a week?
Technically, yes, if you use a no-code wrapper and a simple PDF upload. However, such a bot will likely lack security guardrails, brand customization, and deep integration, making it unsuitable for professional enterprise use.
2. How does using GPT-4 affect the development timeline compared to older models?
Using a foundational model like GPT-4 drastically reduces the time required for NLP training. You don’t need to teach the bot grammar or basic reasoning. The time shifts from “training” to “prompt engineering” and “context management,” generally shortening the initial MVP phase.
3. What is the difference between rule-based and AI chatbot timelines?
Rule-based bots require manual writing of every possible question and answer path, which is front-loaded and tedious. AI bots require less initial scripting but significantly more testing and data curation to prevent hallucinations. Generally, AI bots are faster to prototype but take longer to perfect for compliance.
4. How long does the “training” phase take for a custom chatbot?
For RAG-based systems (most common), “training” is actually indexing, which takes hours. However, fine-tuning a model involves curating datasets and running computational jobs, which can take 2-4 weeks depending on data volume and GPU availability.
5. Who needs to be on the development team?
A typical team includes a Project Manager, an AI/ML Engineer (or Backend Developer), a Conversational Designer/Copywriter, and a QA Specialist. Larger projects also require a Data Scientist and a DevOps engineer.
6. How much time should I allocate for maintenance after launch?
AI chatbots are not “set and forget.” You should allocate 5–10 hours per week initially for a human to review conversation logs, update the knowledge base, and patch any behavioral issues. This time requirement decreases as the bot stabilizes.
Conclusion
So, how long does it take to develop an AI chatbot? For a robust, business-grade solution that protects your brand and actually solves user problems, you should plan for a 3 to 4-month timeline from discovery to full launch. While it is tempting to chase the promise of an overnight AI revolution, the most successful projects prioritize data integrity, security, and user experience over speed.
Developing an AI chatbot is not just a software project; it is an operational transformation. By allocating sufficient time for the discovery and testing phases, you ensure that your investment delivers long-term ROI rather than short-term frustration. Start with a clear MVP, iterate based on real user feedback, and scale your timeline according to the complexity of the intelligence you wish to deploy.
Editor at XS One Consultants, sharing insights and strategies to help businesses grow and succeed.